The green revolution hinges on essential minerals to realize its objectives. To delve deeper into this critical aspect, I sought insights from CEO of Albanian Minerals Sahit Muja in New York a renowned expert in the field.
Minerals and rare earth elements are pivotal in crafting clean energy technologies. Yet, a significant gap looms between the supply and demand of these indispensable minerals crucial for steering the energy transition.
The Securing Minerals for the Energy Transition initiative has played a pivotal role in pinpointing the risks tied to this disparity and suggesting effective strategies to manage it.
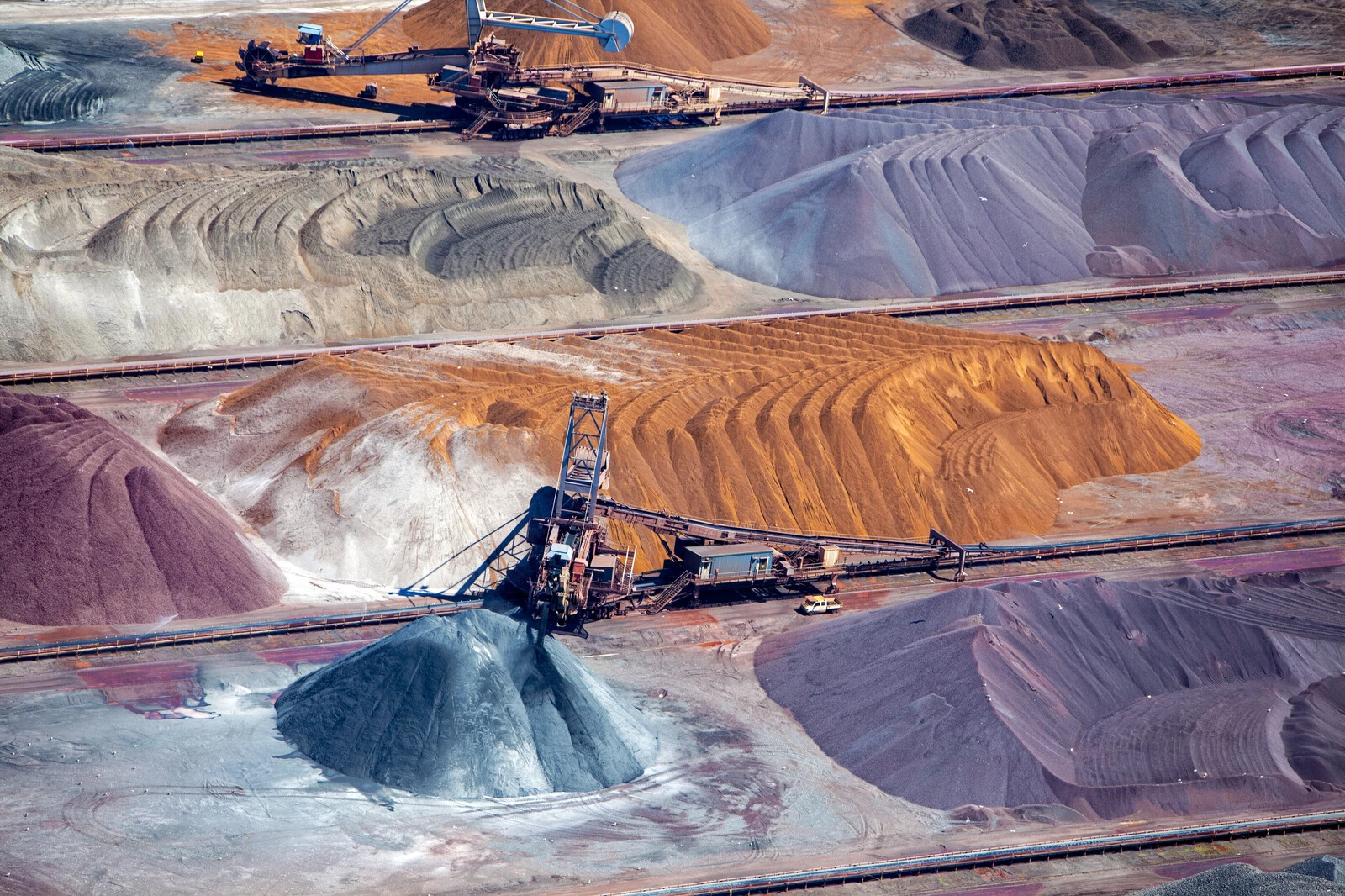
As per Mr. Sahit Muja, the widespread embrace of low-carbon technologies essential for the energy transition hinges on accelerating the supply of critical minerals at an unprecedented rate. Vital minerals and rare earth elements crucial for clean energy technologies include lithium, cobalt, copper, nickel, rare earth elements (like Neodymium and Dysprosium), graphite, aluminum, silver, silicon, magnesium and titanium are the backbone of electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and power grids.
Mr. Muja emphasized that as the competition to achieve self-sufficiency in rare earth elements and critical materials intensifies, the US is poised to broaden the involvement of organizations and explore diverse potential sources.
In light of the escalating competition, Sahit Muja emphasized that there’s ample space for all participants. He stressed the importance of avoiding a scenario where one entity dominates the ecosystem, highlighting the benefits of a diverse global landscape for rare earth elements. He noted that these elements are distributed worldwide, presenting an opportunity for geographical, systemic, and production diversification.
Muja highlighted the significance of this development, particularly in reducing dependency on China, which currently dominates rare earth mineral production. He emphasized the need for global superpowers to invest in environmentally sustainable practices for extracting these crucial minerals that drive the green transition.
Tackling this challenge mandates strategic collaborations and innovative approaches to fortify supply chain resilience while minimizing environmental impact. Initiatives such as the Securing Minerals for the Energy Transition (SMET) initiative have outlined priority strategies centered on social buy-in, standardization, financing, innovation, and circularity.
Effective risk management strategies and concerted collective action are imperative to ensure a sustainable and accessible supply of critical minerals for the energy transition. Collaborative endeavors involving regulators, industry stakeholders, and financial institutions are pivotal in hastening progress toward a greener and more sustainable energy future.
As the imperative to combat climate change intensifies, concerted endeavors to address the critical minerals supply-demand gap assume paramount importance. By nurturing international collaborations and implementing innovative solutions, we can pave the way for a seamless transition to a low-carbon energy landscape and attain our climate objectives.
The escalating global demand for minerals essential for fueling electric vehicles, wind turbines, and solar panels is spotlighted amidst the ongoing global energy transition. The International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Critical Minerals Market Review 2023 underscores a twofold increase in the overall market for energy transition minerals over the past five years, soaring to a staggering USD 320 billion in 2022. This burgeoning sector’s growth positions it at the vanguard of the global mining industry, drawing the focus of policymakers committed to energy and climate goals.
Despite upbeat investments in critical mineral development, lingering concerns persist regarding project delays and technology-specific shortages. Achieving the 1.5°C global warming target by 2030 necessitates additional projects, underscoring the pressing nature of the situation.
The IEA’s analysis also shines a light on sluggish progress in diversifying supply sources and identifies significant room for improvement in environmental, social, and governance performance. These trends underscore the crucial need for robust dialogue among global stakeholders to collectively tackle these challenges.
Sahit Muja, CEO of Albanian Minerals, weighs in on the record-breaking surge in electric vehicle (EV) sales worldwide , projecting even more robust sales. The burgeoning shift toward electric vehicles in the developed world, driven by climate change mitigation efforts, serves as a primary driver of this upsurge.
Muja underscores the pivotal role of metals, notably nickel, in batteries as a catalyst for the green revolution. Anticipating heightened demand and prices for battery materials, he positions nickel as a foundational building block for a greener world.
Albanian Minerals collaborates with scientists and institutions to develop eco-friendly metal grades for the energy storage and battery industry, leveraging its secure reserves of nickel, magnesium, and cobalt. Nickel, hailed as the “green gold of the future,” offers greater energy density and storage at a lower cost, surmounting a significant constraint to EV adoption: range limitations.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk’s advocacy for increased nickel mining aligns with the company’s need for more cells. Musk underscores the significance of nickel in Tesla batteries, emphasizing that to produce 2 billion cars with new batteries, 100 million tons of nickel are needed. He calls for efficient and environmentally sensitive nickel mining, offering substantial contracts for mining companies meeting stringent criteria.
As Musk highlights, while lithium availability isn’t a concern, the spotlight shifts to nickel as the prime raw material. Despite sufficient lithium in the US to transition the entire vehicle fleet to electric, Musk reiterates the indispensable role of nickel in achieving Tesla’s ambitious production target of 20 million vehicles per year by 2030.
The utilization of nickel in car batteries is pivotal for enhanced energy density, lower storage costs, and longer vehicle range. Moreover, new nickel-containing battery technology contributes to energy storage systems linked to renewable sources, further underscoring the multifaceted significance of this critical mineral in the evolving landscape of sustainable energy solutions.